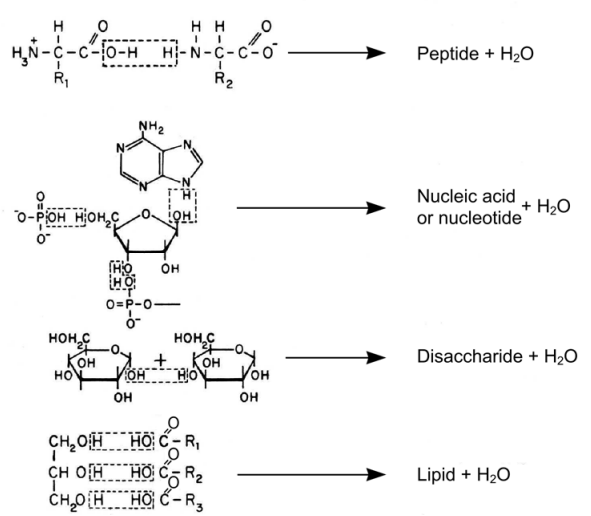
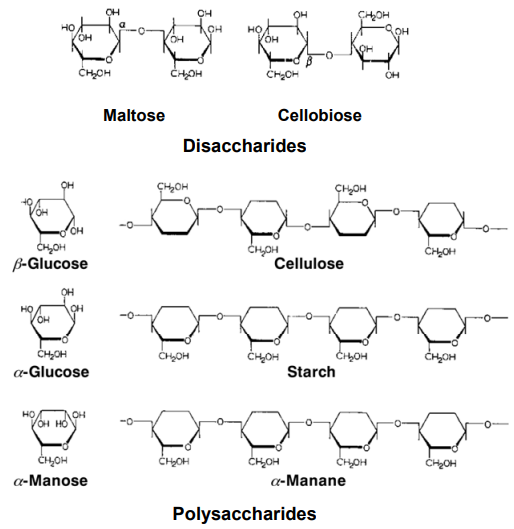
Page 132
image
image
Figure 2–59. Electron micrographs of nuclei. A — nucleus in a cell of mouse pancreas (After De Robertis at al., 1973). 1 — chromatin connected with the nucleolus (2); 3 — nucleoplasm; the arrows indicate pores in the nuclear envelope. B — nucleus in a cell of the dividing area in a root of Zea mays. Bar 0.8 μm (Courtesy of S. Doncheva and G. Ignatov, Institute of Plant Physiology, Sofia). NE — nuclear envelope; N — nucleus; n — nucleolus.
The nucleus is filled up with nucleoplasm limited by a nuclear envelope,
consisting of two membranes — inner and outer. They are separated by a
intermediate space. The nuclear envelope is crossed by pores of diameter
10—20 nm through which nucleic acids, proteins and various other