is formed growing in the direction from 5′ to 3′ end with the incorporation of
nucleotides. This process goes on until another specific nucleotide sequence
is reached — stop-signal i.e. the signal for termination. Then the RNA
polymerase is separated from the DNA-chain matrix and the newly
synthesized mRNA. The hybrid helix RNA—DNA thus formed is unstable, that
is why the initial DNA-helix is restored and the completed RNA chain is
released as a free single-chain molecule (Fig. 2–34).
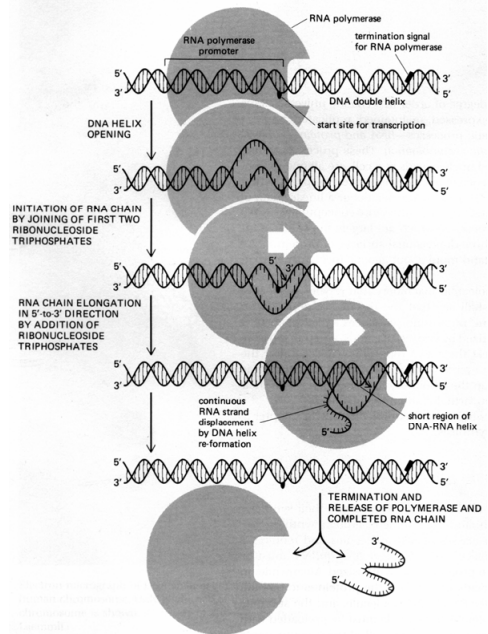
Figure 2–34. Scheme illustrating how RNA polymerase initiated synthesis at the special start signal in DNA, called promotor, and terminates at the stop signal, after which the enzyme and the synthesized new mRNA chain are released. The rate of polymerization at 37°C equals 30 nucleotides in a second. The picture gives an idea of the approximate ratio between the sizes of RNA polymerase and the DNA helix (After Alberts et al., 1989).