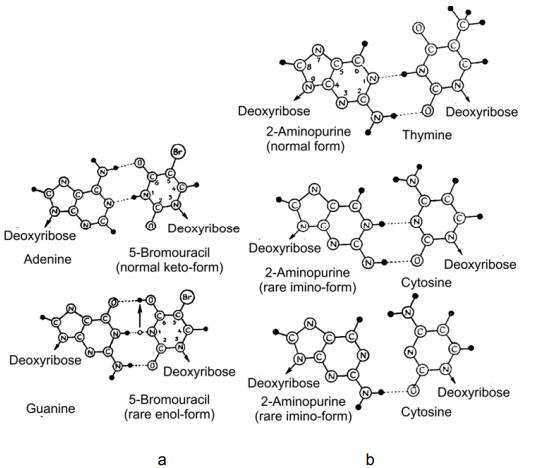
Figure 2–78. Properties of 5-bromouracil (a) and 2-aminopurine (b) relevant to the formation of “incorrect” nucleotide pairs with the bases of DNA. Hydrogen atoms are denoted by black circles, and the bonds between them — by dotted line (After Hayes, 1965).
Under the action of different chemical mutagen factors the bases of
DNA can undergo a modification that leads to inducing of mutations. For
example, nitrous acid (HNO₂) causes an oxidative deamination of the
bases, at that amino groups are substituted for keto groups. Thus, cytosine
is transformed into uracil, adenine — into hypoxantine, and guanine — into
xantine. Thymine is the only, that is not a subject to deamination since it
lacks amino group, and contains a keto group (Fig. 2–79). At that uracil
binds adenine, and xantine and hypoxantine — cytosine.