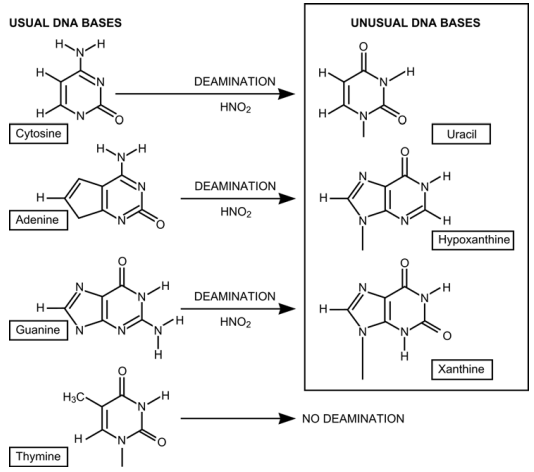
Figure 2–79. Deamination of the usual bases in DNA and formation of unusual ones, leading to disturbances in the correct complementation.
Ultraviolet radiation in the range ~ 260 nm (i.e. wavelength
corresponding to the maximum absorption by DNA) also causes different
alterations in nucleic acids. Among them well-known is the formation of
pyrimidine (mainly thymine) dimers (Fig. 2–80). If they prove to be stable,
they may have an adverse effect on DNA-ability to replicate.
The majority of the mutations are not base substitutions. They
represent large deletions or changes caused by a shifting the frame of
reading (frame shift mutations). The latter are due to an addition or loss of a
certain number of nucleotides in DNA-chain, that leads to mistakes in the
normal reading of codons and therefore — to defects in the translation of
genetic information. Thus, during protein synthesis the correct amino acid
sequence is disturbed.
Except the point mutations, the chromosome and genome mutations
are of great interest. Their molecular bases and mechanisms are less
studied. They are connected with changes in the structure and number of
chromosomes as well as with the ploidy of chromosome set.